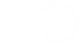Kaspersky Lab has been assisting with incident response efforts. While investigating a cryptocurrency exchange attacked by Lazarus, we made an unexpected discovery. The victim had been infected with the help of a trojanized cryptocurrency trading application, which had been recommended to the company over email. It turned out that an unsuspecting employee of the company had willingly downloaded a third-party application from a legitimate looking website and their computer had been infected with malware known as Fallchill, an old tool that Lazarus has recently switched back to. There have been multiple reports on the reappearance of Fallchill, including one from US-CERT.
To ensure that the OS platform was not an obstacle to infecting targets, it seems the attackers went the extra mile and developed malware for other platforms, including for macOS. A version for Linux is apparently coming soon, according to the website. It’s probably the first time we see this APT group using malware for macOS.
The fact that the Lazarus group has expanded its list of targeted operating systems should be a wake-up call for users of non-Windows platforms.
Trojanized cryptocurrency trading application
Thanks to Kaspersky Lab’s malicious-behavior detection technology, implemented in its endpoint security software, we were able to reassemble the stages of infection and trace them back to their origin. This helped us understand that one of Lazarus’ victims was infected with malware after installing a cryptocurrency trading program. We also confirmed that the user installed this program via a download link delivered over email.
Trojanized trading application for Windows
Including malicious code into distributed software and putting that on a website would be too obvious. Instead, the attackers went for a more elaborate scheme: the trojan code was pushed out in the form of an update for a trading application.
A legitimate-looking application called Celas Trade Pro from Celas Limited showed no signs of malicious behaviour and looked genuine. This application is an all-in-one style cryptocurrency trading program developed by Celas.
When we started this research, any user could download the trading application from the Celas website. Checking the installation package downloaded from the website confirmed the presence of a very suspicious updater.
We have analyzed the following Windows version of the installation package:
MD5: 9e740241ca2acdc79f30ad2c3f50990a
File name: celastradepro_win_installer_1.00.00.msi
File type: MSI installer
Creation time: 2018-06-29 01:16:00 UTC
At the end of the installation process, the installer immediately runs the Updater.exe module with the “CheckUpdate” parameter. This file looks like a regular tool and most likely will not arouse the suspicion of system administrators. After all, it even contains a valid digital signature, which belongs to the same vendor. But the devil is in the detail, as usual.
The code writer developed this project under the codename “jeus”, which was discovered in a PDB path included in the updater and used as unique HTTP multipart message data separator string. Because of this, and the fact that the attacked platforms include Apple macOS, we decided to call this Operation AppleJeus.
Properties of the shady updater tool included in the package are:
MD5: b054a7382adf6b774b15f52d971f3799
File Type: PE32 executable (GUI) Intel 80386, for MS Windows
Known file name: %Program Files%\CelasTradePro\Updater.exe
Link Time: 2018-06-15 10:56:27 UTC
Build path: Z:\jeus\downloader\downloader_exe_vs2010\Release\dloader.pdb
The main purpose of Updater.exe is to collect the victim’s host information and send it back to the server. Upon launch, the malware creates a unique string with the format string template “%09d-%05d” based on random values, which is used as a unique identifier of the infected host. This malware collects process lists, excluding “[System Process]” and “System” processes and gets the exact OS version from the registry value at “HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion”. It seems that such values only exist from Windows 10, so we assume that the author developed and tested it on Windows 10.
- ProductName: Windows OS version
- CurrentBuildNumber: Windows 10 build version
- ReleaseID: Windows 10 version information
- UBR: Sub version of Windows 10 build
- BuildBranch: Windows 10 build branch information
The code encrypts the collected information with the hardcoded XOR key (“Moz&Wie;#t/6T!2y“) before uploading it to the server.
The code sends the victim’s information to a webserver using HTTP and the following URL:
www.celasllc[.]com/checkupdate.php
The server is a legitimate looking website owned by the developer of the program: Celas LLC. At this point we were not able to conclude with high confidence whether the server was compromised by the threat actor or had belonged to the threat actor from the beginning. To learn more about the server, please read the “Infrastructure” section below.
The malware used a hardcoded User-Agent string “Mozilla/5.0 (compatible; MSIE 10.0; Windows NT 6.1; Trident/6.0)” and fixed a multipart form data separator string “jeus“.
Using encryption, the custom separator string wouldn’t be a red flag for a legitimate application, but sending a request with the context-irrelevant string “get_config”, as well as uploading collected system information as “temp.gif”, mimicking a GIF image with a magic number in the header, definitely made us raise our eyebrows.
After successfully uploading data, the updater checks the server response. If the server responds with HTTP code 300, it means the updater should keep quiet and take no action. However, if the response is HTTP code 200, it extracts the payload with base64 and decrypts it using RC4 with another hardcoded key (“W29ab@ad%Df324V$Yd“). The decrypted data is an executable file that is prepended with the “MAX_PATHjeusD” string.
During our research, we found other similar files. One was created on August 3rd and another on August 11th. The PDB path shows that the author keeps improving this updater tool, apparently forked from some stable version released on July 2, 2018 according to the internal directory name.
| Additional trojanized sample #1 | Additional trojanized sample #1 | |
| Installation package MD5 | 4126e1f34cf282c354e17587bb6e8da3 | 0bdb652bbe15942e866083f29fb6dd62 |
| Package creation date | 2018-08-03 09:57:29 | 2018-08-13 0:12:10 |
| Dropped updater MD5 | ffae703a1e327380d85880b9037a0aeb | bbbcf6da5a4c352e8846bf91c3358d5c |
| Updater creation date | 2018-08-03 09:50:08 | 2018-08-11 7:28:08 |
| Updater Build path | H:\DEV\TManager\DLoader\20180702\dloader\WorkingDir\Output\00000009\Release\dloader.pdb | H:\DEV\TManager\DLoader\20180702\dloader\WorkingDir\Output\00000006\Release\dloader.pdb |
Note the TManager directory in the PDB path from the table. It will pop up again in another unexpected place later.
Trojanized trading program for macOS
For macOS users, Celas LLC also provided a native version of its trading app. A hidden “autoupdater” module is installed in the background to start immediately after installation, and after each system reboot. It keeps contacting the command and control (C2) server in order to download and run an additional executable from the server. The communication conforms to the Windows version of the updater and is disguised as an image file upload and download, while carrying encrypted data inside.
We have analyzed the following installation file:
MD5: 48ded52752de9f9b73c6bf9ae81cb429
File Size: 15,020,544 bytes
File Type: DMG disk image
Known file name: celastradepro_mac_installer_1.00.00.dmg
Date of creation: 13 July 2018
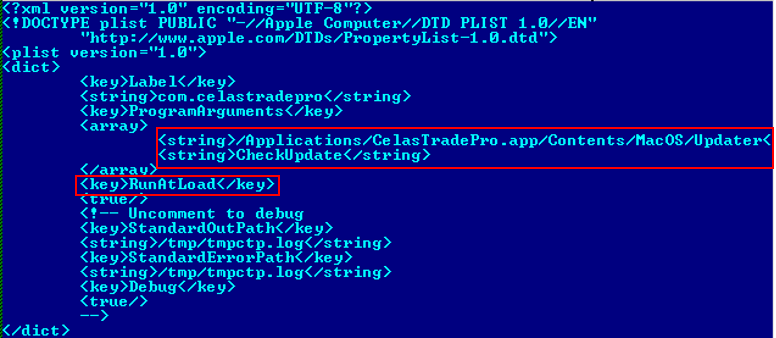
Once the Cellas Trade Pro app is installed on macOS, it starts the Updater application on the system load via a file named “.com.celastradepro.plist” (note that it starts with a dot symbol, which makes it unlisted in the Finder app or default Terminal directory listing). The “Updater” file is passed the “CheckUpdate” parameter on start.
The command-line argument “CheckUpdate” looks redundant from a code analysis perspective: there is no other argument that the application expects. In the absence of all arguments, it doesn’t do anything and quits. This may or may not be way to trick sandboxes that could automatically execute this trojan updater, with no suspicious activity produced without such a “secret” extra argument. The choice of a benign string such as “CheckUpdate” helps it to hide in plain sight of any user or administrator looking into running processes.
The trojanized updater works similar to the Windows version in many ways. Both applications are implemented using a cross-platform QT framework. Upon launch, the downloader creates a unique identifier for the infected host using a “%09d-%06d” format string template. Next, the app collects basic system information, which for macOS is done via dedicated QT classes:
- Host name
- OS type and version
- System architecture
- OS kernel type and version
The process of encrypting and transferring data is the same as in the Windows version. This information is XOR-encrypted with hardcoded 16-byte static key “Moz&Wie;#t/6T!2y”, prepended with GIF89a header and uploaded to the C2 server via HTTP POST and the following URL:
https://www.celasllc[.]com/checkupdate.php
The module relies on a hardcoded User-Agent string for macOS:
User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_12_6) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/66.0.3359.139 Safari/537.36
Once the server replies, it checks the HTTP response code. HTTP response code 300 indicates that the server has no task for the updater and the application terminates immediately. If the HTTP response is code 200, then the updater gets the data in the response, decodes it from base64 encoding and decrypts it using RC4 with the hardcoded static key “W29ab@ad%Df324V$Yd“. It calculates the MD5 of the decoded and decrypted data, which is compared to a value stored inside, to verify the integrity of the transferred file. After that, the payload is extracted and saved to a hardcoded file location “/var/zdiffsec“, sets executable permissions for all users and starts the app with another secret hardcoded command-line argument “bf6a0c760cc642“. Apparently the command-line argument is the way to prevent the detection of its malicious functionality via sandboxes or even reverse engineering. We have previously seen this technique adopted by Lazarus group in 2016 in attacks against banks. As of 2018, it is still using this in almost every attack we investigated.
Downloaded payload
According to data from Kaspersky Security Network, the threat actor delivered the malicious payload using one of the shadowy updaters described above. We found a malicious file created at the same host:
MD5: 0a15a33844c9df11f12a4889ae7b7e4b
File Size: 104,898,560 bytes
File Type: PE32+ executable (GUI) x86-64, for MS Windows
Known file name: C:\Recovery\msn.exe
Link time: 2018-04-19 13:30:19
Note the unusually large size for an executable file. We believe that it was inflated with junk data on purpose to prevent easy download or transfer over the internet.
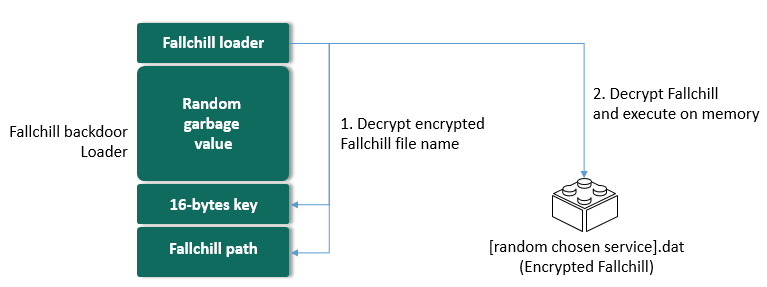
Searching for the reason for the malware’s appearance on the system revealed that there was an additional process responsible for producing several files before this malware was launched, suggesting a trojan dropper in action. The main function of this malware is to implant the Fallchill backdoor loader linked to several files. Upon launch, the malware checks one of the command-line arguments passed to it. The malware chooses one of the service names located in the following registry value as a disguise:
HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Svchost\netsvcs
This value includes a list of several dozen standard system service names.
The randomly chosen service name is used to name the dropped file and newly registered Windows service. Let’s refer to this randomly chosen service name as [service]. The malware contains references to several files inside:
- The file passed as argument: contains a 16-byte key
- msncf.dat: Encrypted configuration data
- msndll.tmp: Encrypted Fallchill loader
- msndll.dat: Encrypted Fallchill backdoor (payload for the loader)
- [service]svc.dll: Fallchill backdoor loader
- [service].dat: Copy of msndll.dat
A mix of the above-mentioned files produces the final backdoor known as Fallchill. A more detailed procedure for technical specialists is as follows:
- Check whether the command-line argument points to a file of 16 byte size.
- Read the file passed via the command-line argument. The contents of this file contains a crypto key, which we will call the main key.
- Open the msncf.dat file (configuration file). If the file size equals 192 bytes, read the content of the file.
- Open msndll.tmp file and decrypt it using the main key.
- Create the [service]svc.dll file and fill it with pseudo-random data.
- The malware fills the file with 10,240 bytes of pseudo-random data, and iterates (rand() % 10 + 10240) times. This is why it produces files which are at least 104,851,000 bytes.
- Copy the 16-byte main key at the end of the [service]svc.dll file.
- Encrypt the [service].dat file name with the main key and append it at the end of [service]svc.dll.
- Overwrite the beginning of [service]svc.dll with data decrypted from msndll.tmp.
- Move msndll.dat file to [service].dat.
- Delete temporary files: msndll.tmp, msncf.dat, msndll.log.
- Timestamp [service]svc.dll and [service].dat files.
- Register [service]svc.dll as a Windows service.
- Save a copy of data from msncf.dat file in the following registry value
HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\TaskConfigs\Description.
Fallchill backdoor loader
We confirmed that the following malware was created on the infected host using the method described above:
Fallchill backdoor loader:
MD5: e1ed584a672cab33af29114576ad6cce
File Size: 104,878,356 bytes
File Type: PE32+ executable (DLL) (console) x86-64, for MS Windows
Known file name: C:\Windows\system32\uploadmgrsvc.dll
Link time: 2018-01-18 01:56:32
Encrypted Fallchill backdoor:
MD5: d8484469587756ce0d10a09027044808
File Size: 143,872 bytes
File Type: encrypted data
Known file name: C:\Windows\system32\uploadmgr.dat
Upon starting, uploadmgrsvc.dll reads 276 bytes from the end of its own executable file. The first 16 bytes of this 276-byte data are used as a decryption key, and the remaining 260 bytes contain the encrypted file path used by the backdoor.
After decryption of the last 260-bytes, the malware retrieves the name or path of the file that contains the actual backdoor body in encrypted form.
The malware reads the specified file and decrypts it using the same decryption routine. This is how the executable code of the backdoor is produced in memory and executed by the loader. Below is the meta information about the decrypted final payload in memory:
MD5: d7089e6bc8bd137a7241a7ad297f975d
File Size: 143,872 bytes
File Type: PE32+ executable (DLL) (GUI) x86-64, for MS Windows
Link Time: 2018-03-16 07:15:31
We can summarize the Fallchill backdoor loading process as follows:
As mentioned previously, the final payload belongs to a Fallchill malware cluster formerly attributed to the Lazarus APT group. Upon launching, this malware resolves the API function addresses at runtime, and reads the C2 server address from the registry value created during the installation stage:
HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\TaskConfigs\Description
If there is no configuration value, the malware falls back to a default C2 server address.
- 196.38.48[.]121
- 185.142.236[.]226
This is a full-featured backdoor that contains enough functions to fully control the infected host. Some of its network protocol commands are described below.
| Command ID | Description |
| 0x8000 | Write current time and configuration data to registry key |
| 0x8001 | Send configuration data |
| 0x8002 | Replace configuration data in the fixed registry value |
| 0x8003 | Execute Windows command, store output in temp file and upload contents to C2 |
| 0x8006 | Show current working directory |
| 0x8007 | Change current working directory |
| 0x8008 | Collect process information |
| 0x8009 | Terminate process |
| 0x8010 | Start new process |
| 0x8011 | Create process with security context of the current user |
| 0x8012 | Connect to specified host/port |
| 0x8013 | Get drive information |
| 0x8014 | Directory listing |
| 0x8015 | Search a file |
| 0x8019 | Write data to a specified file |
| 0x8020 | Read contents of specified file and upload to C2 server |
| 0x8021 | Compress multiples files to a temp file (name start with ZD) and upload to C2 |
| 0x8023 | Wipe specific file |
| 0x8025 | Copy file time from another file time (timestamping) |
| 0x8026 | Shutdown malware service and self-delete |
| 0x8043 | Send “Not Service” unicode string to C2 server (communication test?). |
This set of capabilities is very common for many Lazarus backdoors, which have been seen in other attacks against banks and financial industry in the past years.
Infrastructure
While working on the incident of the cryptocurrency company’s breach, we were curious about the legal status of the Celas LLC company that developed this trojanized trading application.
The website had a valid SSL certificate issued by Comodo CA. However, note that the certificate from this webserver mentions “Domain Control Validated”, which is a weak security verification level for a webserver. It does not mean validation of the identity of the website’s owner, nor of the actual existence of the business. When certification authorities issue this kind of certificate they only check that the owner has a certain control over the domain name, which can be abused in certain ways.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
Certificate:
Data:
Version: 3 (0x2)
Serial Number:
22:a6:49:c1:ae:61:3f:58:5a:a5:e3:cb:8b:23:f0:61
Signature Algorithm: sha256WithRSAEncryption
Issuer: C=GB, ST=Greater Manchester, L=Salford, O=COMODO CA Limited, CN=COMODO RSA Domain Validation Secure Server CA
Validity
Not Before: May 29 00:00:00 2018 GMT
Not After : May 29 23:59:59 2019 GMT
Subject: OU=Domain Control Validated, OU=PositiveSSL, CN=celasllc.com
Subject Public Key Info:
Public Key Algorithm: rsaEncryption
Public–Key: (2048 bit)
Modulus:
00:de:0f:58:f2:68:07:d2:0f:43:5a:07:c6:53:b7:
4a:b4:1c:4c:71:4f:a1:4e:80:e3:5a:ec:3b:90:a7:
91:ca:42:49:71:ba:da:33:4c:e4:4f:1f:86:d9:30:
32:a0:b1:f4:b2:f2:9c:28:97:7c:81:0f:02:d0:9c:
36:f6:9c:d6:f9:b5:ca:23:ba:1b:84:e4:0d:8c:9f:
— Redacted —
|
Below is the WHOIS record of the “celasllc.com” domain. The domain name was registered by an individual named “John Broox” with registrant email address “johnbroox200@gmail[.]com”.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
Registrant Name: John Broox
Registrant Organization:
Registrant Street: 2141 S Archer Ave
Registrant City: Chicago
Registrant State/Province: Illinois
Registrant Postal Code: 60601
Registrant Country: US
Registrant Phone: +1.8133205751
Registrant Email: johnbroox200@gmail[.]com
…..
Name Server: 1a7ea920.bitcoin–dns.hosting
Name Server: a8332f3a.bitcoin–dns.hosting
Name Server: ad636824.bitcoin–dns.hosting
Name Server: c358ea2d.bitcoin–dns.hosting
|
The same name of “John Broox” was used inside the installation package of the macOS version of the trading application. The Info.plist properties file describes the package as follows:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
|
<?xml version=“1.0” encoding=“UTF-8”?>
<!DOCTYPE plist PUBLIC “-//Apple//DTD PLIST 1.0//EN” “http://www.apple.com/DTDs/PropertyList-1.0.dtd”>
<plist version=“1.0”>
<dict>
<key>CFBundleVersion</key>
<string>1.00.00</string>
<key>CFBundleName</key>
<string>Celas Trade Pro</string>
<key>CFBundleIconFile</key>
<string>CelasTradePro</string>
<key>CFBundlePackageType</key>
<string>APPL</string>
<key>CFBundleGetInfoString</key>
<string>Developed by John Broox. CELAS LLC</string>
<key>CFBundleSignature</key>
<string>QTCELASTRADE</string>
<key>CFBundleExecutable</key>
<string>CelasTradePro</string>
<key>CFBundleIdentifier</key>
<string>com.celasllc.CelasTradePro</string>
<key>NSPrincipalClass</key>
<string>NSApplication</string>
<key>NSHighResolutionCapable</key>
<string>True</string>
<key>LSMinimumSystemVersion</key>
<string>10.10.0</string>
</dict>
</plist>
|
It looks at first sight like a legitimate WHOIS record, but something doesn’t really add up here. The domain celasllc.com was the only domain registered with this email address and was exclusively used for domain registration.
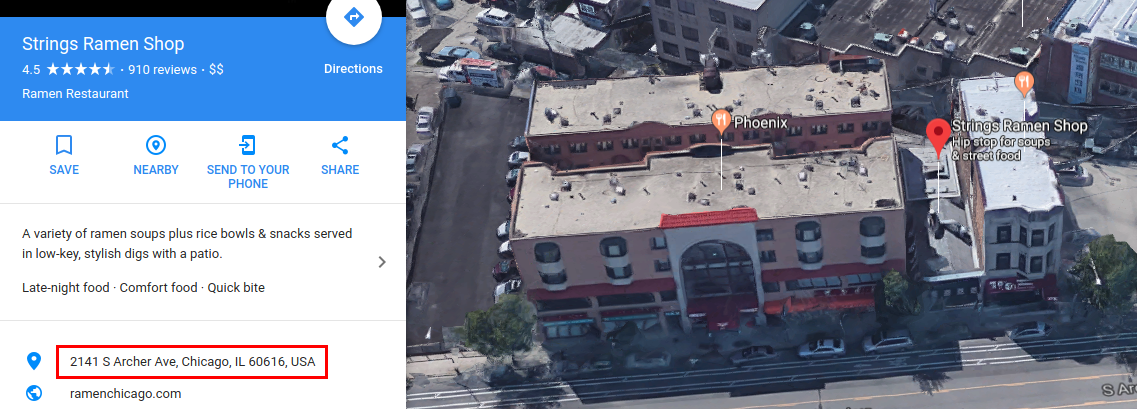
The registrant used the Domain4Bitcoins service to register this domain, apparently paying with cryptocurrency. According to open-source intelligence, the address of the WHOIS information is fake, unless it’s the owner of a ramen shop running a cryptocurrency exchange software development studio on the side.
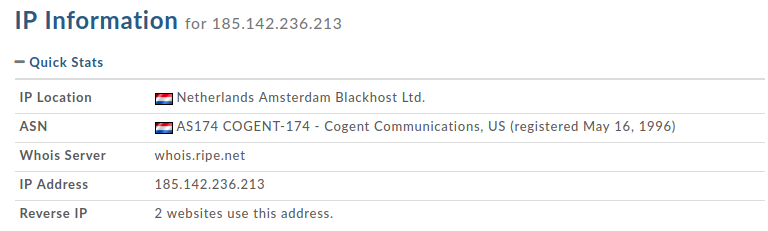
The server hosting celasllc.com (185.142.236.213) belongs to the Blackhost ISP in the Netherlands.
Coincidentally, the Fallchill malware authors also preferred to use the same hosting company to host their C2 server. Moreover, the Celas LLC web server and one of the C2 servers of the Fallchill malware are located in the same network segment of this ISP:
- Celas LLC infrastructure:
- 185.142.236.213: Netherlands Blackhost Ltd. AS174 COGENT-174
- Fallchill malware C2 server:
- 196.38.48[.]121: South Africa Internet Solutions AS3741
- 185.142.236[.]226: Netherlands Blackhost Ltd. AS174 COGENT-174
- Additional attacker’s server from telemetry
- 80.82.64[.]91: Seychelles Incrediserve Ltd AS29073
- 185.142.239[.]173: Netherlands Blackhost Ltd. AS174 COGENT-174
However, when you look into Celas Trading Pro application’s digital signature, including its “Updater”, you will find that this certificate was also issued by Comodo CA, which refers to a company address in the United States.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
Certificate:
Data:
Version: 3 (0x2)
Serial Number:
9a:73:55:0b:83:76:86:3b:d9:43:0f:aa:8b:5a:29:87
Signature Algorithm: sha256WithRSAEncryption
Issuer: C=GB, ST=Greater Manchester, L=Salford, O=COMODO CA Limited, CN=COMODO RSA Code Signing CA
Validity
Not Before: May 21 00:00:00 2018 GMT
Not After : May 21 23:59:59 2019 GMT
Subject: C=US/postalCode=49319, ST=Michigan, L=Cedar Springs/street=15519 WHITE CREEK AVE NE, O=CELAS LLC, CN=CELAS LLC
Subject Public Key Info:
Public Key Algorithm: rsaEncryption
Public–Key: (2048 bit)
Modulus:
00:b6:31:7a:c6:68:2f:d2:03:f2:e9:61:c4:86:4f:
46:62:e7:a6:d7:7c:bd:e6:9f:a8:83:2c:a6:44:43:
92:da:b7:ea:cc:3d:3e:35:20:3f:9c:57:46:1c:d1:
65:b8:28:50:29:cd:29:11:e8:56:59:85:e5:0f:19:
|
According to open-source data, this address doesn’t belong to a real business, and looks on maps like a meadow with a small forest and small real estate offering nearby.
Pivoting the infrastructure a little further brings up some more suspicious things. It appears that the domain referred to two IPs, one of which was linked to a few other suspicious domains, according to PassiveDNS.
The owners of the linked infrastructural elements preferred to use several interesting services for hosting domain registration. All these service providers offer a certain level of anonymity to their customers. Most of them accept Bitcoins as a main payment method to keep their customers anonymous. This is very uncommon for companies running a legitimate business.
Hosting services linked to Celas LLC:
- Blackhost (https://black.host/)
- Liberty VPS (https://libertyvps.net/)
Domain registration services linked to Celas LLC:
- Domains4Bitcoins (https://www.domains4bitcoins.com/)
- NameCheap (https://www.namecheap.com/)
- ChangeIP (https://www.changeip.com/)
- Njalla (https://njal.la/)
All the facts above can make the more sceptical among us doubt the intentions of Celas LLC and the legitimacy of this business. Of course, these facts alone would not be enough to accuse Celas LLC of committing a crime.
Attribution
Kaspersky Lab has previously attributed the Fallchill malware cluster to Lazarus group when it attacked the financial sector around the world. It was also confirmed by other security vendors, and the national CERT of US.
RC4 key from the older Fallchill
Fallchill malware uses a RC4 algorithm with a 16-byte key to protect its communications. The key extracted from the Fallchill variant used in the current attack is DA E1 61 FF 0C 27 95 87 17 57 A4 D6 EA E3 82 2B.
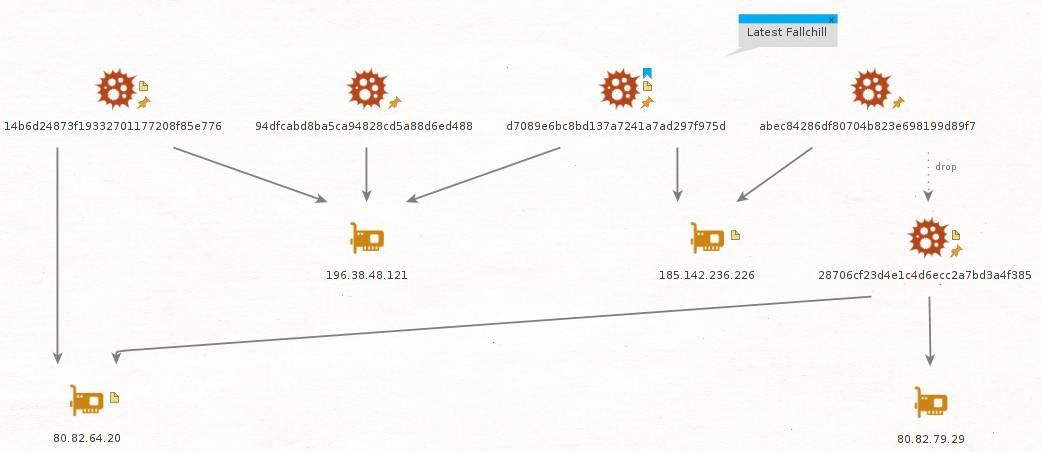
We were able to confirm that some of older Fallchill malware variants used exactly the same RC4 key. Below are Fallchill malware samples that used the same key (the compilation timestamp may indicate the date of malware creation).
| MD5 | Timestamp |
| 81c3a3c5a0129477b59397173fdc0b01 | 2017-05-26 23:37:04 |
| 6cb34af551b3fb63df6c9b86900cf044 | 2017-06-09 17:24:30 |
| 21694c8db6234df74102e8b5994b7627 | 2017-11-07 17:54:19 |
| 5ad7d35f0617595f26d565a3b7ebc6d0 | 2015-10-24 01:52:11 |
| c501ea6c56ba9133c3c26a7d5ed4ce49 | 2017-06-09 03:59:43 |
| cafda7b3e9a4f86d4bd005075040a712 | 2017-11-07 17:54:33 |
| cea1a63656fb199dd5ab90528188e87c | 2017-06-12 19:25:31 |
| 6b061267c7ddeb160368128a933d38be | 2017-11-09 17:18:06 |
| 56f5088f488e50999ee6cced1f5dd6aa | 2017-06-13 08:17:51 |
| cd6796f324ecb7cf34bc9bc38ce4e649 | 2016-04-17 03:26:56 |
Same C2 server with older Fallchill
We have confirmed that the C2 server addresses (196.38.48[.]121, 185.142.236[.]226) used in this attack have been used by the older variant of Fallchill.
| MD5 | Timestamp |
| 94dfcabd8ba5ca94828cd5a88d6ed488 | 2016-10-24 02:31:18 |
| 14b6d24873f19332701177208f85e776 | 2017-06-07 06:41:27 |
| abec84286df80704b823e698199d89f7 | 2017-01-18 04:29:29 |
Apparently, the attackers using the Fallchill malware continue to reuse code and C2 server infrastructure over and over again.
According to Kaspersky Security Network, Fallchill was not the only malware used in this attack. There was another backdoor that was used by the threat actor. We omit a full description of this backdoor in the current report to keep the write-up to an acceptable length, but we would like to highlight two important things discovered in it. First, this backdoor was created on 2018-07-12 and revealed an already familiar directory, “TManager”, which we previously saw in the Updater.exe application from the Cellas Trading Pro suite:
H:\DEV\TManager\all_BOSS_troy\T_4.2\T_4.2\Server_\x64\Release\ServerDll.pdb
Second, what is probably one of the most interesting findings to come from this additional backdoor was discovered hidden in hardcoded headers used to communicate with C2 server. The Accept-Language HTTP header string revealed a language code associated with North Korea. In our experience, this is something we normally don’t see in malware.
Accept-Language: ko-kp,ko-kr;q=0.8,ko;q=0.6,en-us;q=0.4,en;q=0.2
Conclusions
The Lazarus APT group’s continuous attacks on the financial sector are not much of a surprise to anyone. A lot of research has been done and published about such attacks. However, we think this case makes a difference. Recent investigation shows how aggressive the group is and how its strategies may evolve in the future.
First of all, Lazarus group has entered a new platform: macOS. There is steadily growing interest in macOS from ordinary users, especially in IT companies. Many developers and engineers are switching to using macOS. Apparently, in the chase after advanced users, software developers from supply chains and some high profile targets, threat actors are forced to have macOS malware tools. We believe that in the future Lazarus is going to support all platforms that software developers are using as a base platform, because compromising developers opens many doors at once.
We cannot say with full certainty whether Celas LLC was compromised and the threat actor abused it to push malware through an update mechanism. However, the multiple successful Lazarus attempts to compromise supply chain companies suggest that it will keep exploring this infection method. From all angles, the Celas LLC story looks like the threat actor has found an elaborate way to create a legitimate looking business and inject a malicious payload into a “legitimate looking” software update mechanism. Sounds logical: if one cannot compromise a supply chain, why not to make fake one?
This should be a lesson to all of us and a wake-up call to businesses relying on third-party software. Do not automatically trust the code running on your systems. Neither good looking website, nor solid company profile nor the digital certificates guarantee the absence of backdoors. Trust has to be earned and proven. Stay safe!